
1. Introduction to C276 Hastelloy Alloy
Hastelloy C276, also known as UNS N10276 or Werkstoff Nr. 2.4819, is a nickel-molybdenum-chromium superalloy with tungsten additions, designed for exceptional corrosion resistance in severe environments. Developed by Haynes International, it is widely regarded as one of the most versatile corrosion-resistant alloys available. Its unique chemical composition enables it to withstand aggressive chemical environments, including oxidizing and reducing conditions, making it a preferred material in industries such as chemical processing, pollution control, pulp and paper production, and marine engineering.
The alloy’s low carbon content minimizes carbide precipitation during welding, ensuring that corrosion resistance is maintained in as-welded structures. Its resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking further enhances its suitability for harsh applications. Hastelloy C276 is available in various forms, including seamless and welded pipes, tubes, sheets, plates, bars, and fittings, with pipes being a critical component in many industrial systems.
This analysis focuses on C276 Hastelloy alloy steel pipes, detailing their specifications, properties, and applications, with a scientific comparison to equivalent materials and a comprehensive breakdown of pipe sizes and standards.
2. Specifications of C276 Hastelloy Alloy Steel Pipe
2.1 Standards
Hastelloy C276 pipes are manufactured in accordance with several international standards to ensure quality and compatibility. The primary standards include:
-
ASTM B622: Seamless Nickel and Nickel-Cobalt Alloy Pipe and Tube
-
ASTM B619: Welded Nickel and Nickel-Cobalt Alloy Pipe
-
ASTM B626: Welded Nickel and Nickel-Cobalt Alloy Tube
-
ASME SB622: Seamless Nickel and Nickel-Cobalt Alloy Pipe and Tube
-
ASME SB619: Welded Nickel and Nickel-Cobalt Alloy Pipe
-
DIN 17751: Nickel and Nickel Alloy Seamless and Welded Tubes
-
ISO 6207: Seamless Nickel and Nickel Alloy Tubes
-
VdTüV 400/12.98: Material Specification for Nickel Alloys
These standards ensure that Hastelloy C276 pipes meet stringent requirements for chemical composition, mechanical properties, and dimensional tolerances.
2.2 Outer Diameter (OD)
The outer diameter of Hastelloy C276 pipes varies depending on the application and manufacturing process. Common OD ranges include:
-
Seamless Pipes: 1/8” (3.175 mm) to 24” (609.6 mm)
-
Welded Pipes: Up to 150” (3810 mm) for large-diameter pipes
-
Tubes: 1/16” (1.59 mm) to 4” (101.6 mm)
Custom diameters are available based on specific project requirements.
2.3 Wall Thickness
Wall thickness is specified by schedule numbers (e.g., SCH 5, SCH 10, SCH 40, SCH 80, SCH 160) or in millimeters. Typical thickness ranges are:
-
Seamless Pipes: 0.5 mm to 50 mm
-
Welded Pipes: 0.5 mm to 60 mm
-
Tubes: 0.5 mm to 10 mm
The wall thickness affects the pipe’s pressure rating and mechanical strength.
2.4 Length
Hastelloy C276 pipes are available in standard and custom lengths:
-
Single Random Length: 4.8 m to 7.3 m (16 ft to 24 ft)
-
Double Random Length: 11.8 m to 13.7 m (38 ft to 45 ft)
-
Cut-to-Length: As per customer specifications, typically ranging from 0.5 m to 12 m
2.5 Manufacturing Techniques
Hastelloy C276 pipes are produced using various techniques:
-
Seamless: Hot extrusion or cold drawing, ensuring uniform structure and high strength.
-
Welded: Electric Resistance Welding (ERW), Electric Fusion Welding (EFW), or Submerged Arc Welding (SAW), suitable for larger diameters.
-
Fabricated: Formed from plates or sheets, often for custom shapes or sizes.
2.6 Surface Finish
Surface finishes enhance the pipe’s corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Common finishes include:
-
Annealed and Pickled: Smooth, oxide-free surface for enhanced corrosion resistance.
-
Polished: Mirror-like finish for aesthetic applications or low-friction requirements.
-
Mill Finish: As-produced surface, suitable for industrial applications.
-
Coated: Epoxy or PTFE coatings for additional protection in specific environments.
2.7 Grade (ASTM/UNS)
The alloy is designated as:
-
-
ASTM: Hastelloy C276
-
UNS: N10276
-
Werkstoff Nr.: 2.4819
-
EN: NiMo16Cr15W
-
GOST: ХН65МВУ
-
JIS: NW 0276
-
3. Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of Hastelloy C276 is critical to its performance. The alloy is a nickel-based superalloy with significant molybdenum, chromium, and tungsten content. The following table outlines the typical composition:
|
Element
|
Percentage (%)
|
|---|---|
|
Nickel (Ni)
|
55.0 – 57.0 (Balance)
|
|
Molybdenum (Mo)
|
15.0 – 17.0
|
|
Chromium (Cr)
|
14.5 – 16.5
|
|
Iron (Fe)
|
4.0 – 7.0
|
|
Tungsten (W)
|
3.0 – 4.5
|
|
Cobalt (Co)
|
2.5 (max)
|
|
Manganese (Mn)
|
1.0 (max)
|
|
Carbon (C)
|
0.01 (max)
|
|
Silicon (Si)
|
0.08 (max)
|
|
Phosphorus (P)
|
0.04 (max)
|
|
Sulfur (S)
|
0.03 (max)
|
|
Vanadium (V)
|
0.35 (max)
|
Analysis of Composition
-
Nickel (Ni): Provides a stable austenitic structure and enhances corrosion resistance in reducing environments.
-
Molybdenum (Mo): Improves resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly in chloride-containing environments.
-
Chromium (Cr): Enhances resistance to oxidizing media, such as nitric acid.
-
Tungsten (W): Increases resistance to localized corrosion and improves overall strength.
-
Low Carbon (C): Minimizes carbide precipitation during welding, preventing intergranular corrosion.
-
Iron (Fe): Balances cost and mechanical properties but kept low to avoid compromising corrosion resistance.
4. Material Properties
Hastelloy C276 exhibits exceptional mechanical, physical, and corrosion-resistant properties, making it suitable for demanding applications.
4.1 Mechanical Properties
The following table summarizes the mechanical properties of Hastelloy C276 in the annealed condition:
|
Property
|
Value
|
|---|---|
|
Tensile Strength
|
690 MPa (100 ksi) min
|
|
Yield Strength (0.2% offset)
|
283 MPa (41 ksi) min
|
|
Elongation
|
40% min
|
|
Hardness (Rockwell B)
|
87 max
|
|
Elastic Modulus
|
205 GPa (29.7 x 10⁶ psi)
|
-
Tensile Strength: Ensures the alloy can withstand high stresses in aggressive environments.
-
Yield Strength: Indicates good ductility, allowing deformation without fracture.
-
Elongation: High elongation ensures formability and resistance to brittle failure.
-
Hardness: Moderate hardness allows machining while maintaining wear resistance.
4.2 Physical Properties
|
Property
|
Value
|
|---|---|
|
Density
|
8.89 g/cm³ (0.321 lb/in³)
|
|
Melting Point
|
1325 – 1370°C (2417 – 2500°F)
|
|
Specific Heat Capacity
|
427 J/kg·K (0.102 Btu/lb·°F)
|
|
Thermal Conductivity
|
10.2 W/m·K (70.6 Btu·in/hr·ft²·°F)
|
|
Electrical Resistivity
|
1.23 µΩ·m (740 µΩ·in)
|
-
Density: Relatively high due to the nickel and molybdenum content, affecting weight considerations in design.
-
Melting Point: High melting range ensures stability in high-temperature applications.
-
Thermal Conductivity: Moderate, suitable for heat exchanger applications.
-
Electrical Resistivity: High resistivity makes it less suitable for electrical applications but ideal for corrosion-resistant components.
4.3 Corrosion Resistance
Hastelloy C276 is renowned for its corrosion resistance in a wide range of environments:
-
Pitting and Crevice Corrosion: Exceptional resistance due to high molybdenum and tungsten content, particularly in chloride-rich environments (e.g., seawater, wet chlorine gas).
-
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC): Resistant to SCC in high-temperature, chloride-containing environments.
-
Oxidizing Media: Chromium content provides resistance to oxidizing acids like nitric acid.
-
Reducing Media: Nickel and molybdenum enhance performance in reducing acids like hydrochloric and sulfuric acid.
-
Intergranular Corrosion: Low carbon content prevents carbide precipitation, ensuring corrosion resistance in welded structures.
4.4 Weldability
Hastelloy C276 is highly weldable using standard techniques such as:
-
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG)
-
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG)
-
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
The low carbon content and resistance to grain boundary precipitation eliminate the need for post-weld heat treatment in most cases, making it ideal for as-welded applications.
4.5 Machinability
Hastelloy C276 is moderately difficult to machine due to its work-hardening tendencies and high shear strength. Key considerations include:
-
Tooling: Use carbide or high-speed steel tools with positive rake angles.
-
Cutting Speed: Low to moderate speeds to minimize heat generation.
-
Coolant: Adequate coolant to reduce tool wear and improve surface finish.
5. Equivalent Materials
Hastelloy C276 is often compared to other nickel-based alloys with similar corrosion resistance. The following table lists equivalent or comparable materials:
|
Alloy
|
UNS
|
Werkstoff Nr.
|
Key Features
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Hastelloy C276
|
N10276
|
2.4819
|
Versatile corrosion resistance, excellent in both oxidizing and reducing media.
|
|
Hastelloy C22
|
N06022
|
2.4602
|
Superior resistance to oxidizing media, slightly better weldability.
|
|
Inconel 625
|
N06625
|
2.4856
|
High strength, good corrosion resistance, but less effective in reducing acids.
|
|
Monel 400
|
N04400
|
2.4360
|
Excellent in seawater, but limited resistance to acids compared to C276.
|
|
Alloy 825
|
N08825
|
2.4858
|
Good corrosion resistance, but less effective in severe environments.
|
Comparative Analysis
-
Hastelloy C276 vs. C22:
-
C276: Better resistance to reducing environments (e.g., hydrochloric acid) due to higher molybdenum content.
-
C22: Superior in oxidizing environments (e.g., nitric acid) and slightly better weldability due to lower iron content.
-
Applications: C276 is preferred for versatile applications, while C22 is used in highly oxidizing conditions.
-
-
Hastelloy C276 vs. Inconel 625:
-
C276: Superior corrosion resistance in aggressive chemical environments.
-
Inconel 625: Higher strength and better fatigue resistance, suitable for high-temperature structural applications.
-
Applications: C276 for chemical processing; Inconel 625 for aerospace and high-temperature environments.
-
-
Hastelloy C276 vs. Monel 400:
-
C276: Far superior in acidic and chloride environments.
-
Monel 400: Excellent in seawater and alkaline conditions but lacks resistance to strong acids.
-
Applications: C276 for chemical plants; Monel 400 for marine and desalination systems.
-
-
Hastelloy C276 vs. Alloy 825:
-
C276: Better resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in severe environments.
-
Alloy 825: Cost-effective for less aggressive conditions but less versatile.
-
Applications: C276 for extreme conditions; Alloy 825 for moderate corrosion environments.
-
6. Pipe Sizes and Schedules
Hastelloy C276 pipes are available in a wide range of sizes and schedules to meet diverse application requirements. The following tables provide detailed size and schedule information.
6.1 Nominal Pipe Sizes (NPS)
|
NPS (inches)
|
OD (mm)
|
Common Schedules
|
Applications
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
1/8
|
10.3
|
SCH 10, 40, 80
|
Small-diameter chemical lines
|
|
1/2
|
21.3
|
SCH 10, 40, 80, 160
|
Process piping, heat exchangers
|
|
1
|
33.4
|
SCH 10, 40, 80, 160
|
General chemical processing
|
|
2
|
60.3
|
SCH 10, 40, 80, 160
|
Pollution control systems
|
|
4
|
114.3
|
SCH 10, 40, 80
|
Large-diameter process lines
|
|
12
|
323.8
|
SCH 10, 40, 80
|
Industrial waste treatment
|
|
24
|
609.6
|
SCH 10, 40
|
Large-scale chemical reactors
|
6.2 Wall Thickness by Schedule
|
Schedule
|
Wall Thickness (mm)
for NPS 1” (33.4 mm OD)
|
Pressure Rating (psi)
|
|---|---|---|
|
SCH 5
|
1.65
|
870
|
|
SCH 10
|
2.77
|
1440
|
|
SCH 40
|
3.38
|
1900
|
|
SCH 80
|
4.55
|
2760
|
|
SCH 160
|
6.35
|
4100
|
6.3 Pipe Weight Calculation
The weight of Hastelloy C276 pipes can be calculated using the formula:
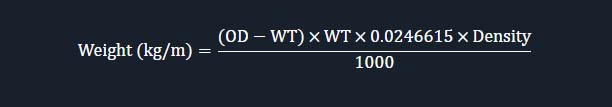
Where:
-
OD = Outer Diameter (mm)
-
WT = Wall Thickness (mm)
-
Density = 8.89 g/cm³
Example Calculation: For a 2” NPS (60.3 mm OD) pipe with SCH 40 (4.55 mm WT):
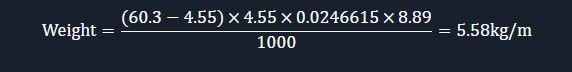
7. Applications of Hastelloy C276 Pipes
Hastelloy C276 pipes are used in industries requiring high corrosion resistance and reliability. Key applications include:
-
Chemical Processing: Reactors, heat exchangers, and piping for handling acids (hydrochloric, sulfuric, nitric).
-
Pollution Control: Flue gas desulfurization systems, scrubbers, and stack liners.
-
Pulp and Paper: Digesters and bleach plants.
-
Marine Engineering: Seawater piping and offshore oil drilling equipment.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Piping for sterile and corrosive processes.
-
Oil and Gas: Sour gas wells and equipment exposed to hydrogen sulfide.
-
Waste Treatment: Piping for handling corrosive waste streams.
8. Scientific Analysis and Comparison
8.1 Corrosion Resistance Comparison
The following table compares the corrosion resistance of Hastelloy C276 with other alloys in various environments:
|
Environment
|
Hastelloy C276
|
Hastelloy C22
|
Inconel 625
|
Monel 400
|
Alloy 825
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Hydrochloric Acid (10%)
|
Excellent
|
Good
|
Moderate
|
Poor
|
Moderate
|
|
Sulfuric Acid (50%)
|
Excellent
|
Excellent
|
Good
|
Poor
|
Good
|
|
Nitric Acid (65%)
|
Good
|
Excellent
|
Good
|
Poor
|
Moderate
|
|
Seawater (Chlorides)
|
Excellent
|
Excellent
|
Good
|
Excellent
|
Good
|
|
Pitting Resistance (PREN*)
|
45
|
47
|
40
|
26
|
31
|
*PREN (Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number) = %Cr + 3.3 × %Mo + 16 × %N
8.2 Mechanical Property Comparison
|
Alloy
|
Tensile Strength (MPa)
|
Yield Strength (MPa)
|
Elongation (%)
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Hastelloy C276
|
690
|
283
|
40
|
|
Hastelloy C22
|
690
|
310
|
45
|
|
Inconel 625
|
830
|
415
|
30
|
|
Monel 400
|
550
|
240
|
40
|
|
Alloy 825
|
590
|
220
|
30
|
8.3 Cost Analysis
Hastelloy C276 is a premium alloy, with prices ranging from $40 to $60 per kg, depending on market conditions and specifications. Compared to other alloys:
-
Hastelloy C22: Slightly higher cost due to enhanced properties.
-
Inconel 625: Comparable cost but less versatile in chemical environments.
-
Monel 400: Lower cost but limited applications.
-
Alloy 825: More cost-effective but less resistant in extreme conditions.
8.4 Case Study: Chemical Processing Reactor
A chemical processing plant used Hastelloy C276 pipes in a reactor exposed to 20% hydrochloric acid at 80°C. Over five years, the pipes showed negligible corrosion (0.01 mm/year), compared to stainless steel 316L, which failed within six months (corrosion rate: 1.2 mm/year). This demonstrates C276’s superior performance in reducing environments.
9. Conclusion
Hastelloy C276 alloy steel pipe is a high-performance material designed for extreme corrosion resistance and mechanical reliability. Its unique chemical composition, with high nickel, molybdenum, and chromium content, ensures versatility in both oxidizing and reducing environments. The alloy’s low carbon content and resistance to grain boundary precipitation make it ideal for welded applications without post-weld heat treatment.
Compared to equivalent materials like Hastelloy C22, Inconel 625, Monel 400, and Alloy 825, Hastelloy C276 offers a balanced combination of corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and weldability, making it the preferred choice for chemical processing, pollution control, and marine applications. Its availability in various sizes, schedules, and surface finishes further enhances its adaptability.




You must be logged in to post a comment.