ANSI B16.5 Weld Neck Pipe Flange: Scientific and Detailed Analysis with Tables
SEO Title: “ANSI B16.5 Weld Neck Pipe Flange: In-Depth Guide with Technical Tables”
Meta Description: “Discover the ANSI B16.5 Weld Neck Pipe Flange, its dimensions, material grades, pressure ratings, and applications in this 3500+ word detailed technical analysis.”
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of Weld Neck Flanges
- Key Features of Weld Neck Pipe Flanges
- Material Grades and Specifications
- Dimensions and Tolerances (with Comprehensive Tables)
- Pressure-Temperature Ratings (with Detailed Tables)
- Facing Types for Weld Neck Pipe Flanges
- Manufacturing Process
- Applications of Weld Neck Flanges
- Advantages of Using Weld Neck Flanges
- Comparison with Other Flange Types
- Installation and Welding Guidelines
- Inspection and Maintenance Procedures
- Environmental and Economic Considerations
- Frequently Asked Questions
1. Introduction
The ANSI B16.5 Weld Neck Pipe Flange is an indispensable component in high-pressure piping systems. Designed with a long tapered hub, this flange transitions stress from the flange to the pipe, minimizing stress concentration at the base. Such features make it a top choice for critical systems where reliability and durability are paramount. Available in sizes ranging from ½” to 96″, weld neck flanges are adaptable to various industrial needs.
2. Overview of Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges are unique in their ability to form robust, leak-proof connections in pipelines. These flanges are welded directly to the pipe, ensuring seamless stress transfer and alignment of the pipe bore and flange. The flange’s inner diameter matches the pipe’s inner diameter, reducing flow turbulence and erosion.
3. Key Features of Weld Neck Pipe Flanges
- Stress Distribution: The tapered hub design transfers stress evenly to the pipe.
- Leak Resistance: Full penetration welding ensures a tight seal.
- Raised, Flat, or RTJ Facing: Different facings meet varied application needs.
- Durability: Suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosive environments.
4. Material Grades and Specifications
ABTER Steel Company manufactures weld neck flanges in various materials, including:
| Material | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Cost-effective, high strength | General-purpose pipelines |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, durable | Food processing, chemical plants |
| Alloy Steel | High-temperature and pressure capabilities | Power plants, oil refineries |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | Combines strength and corrosion resistance | Marine and offshore applications |
Specifications
Weld neck flanges adhere to standards like:
- ANSI B16.5: For nominal pipe sizes ½” to 24”.
- ASME B16.47: For larger flanges, Series A and B.
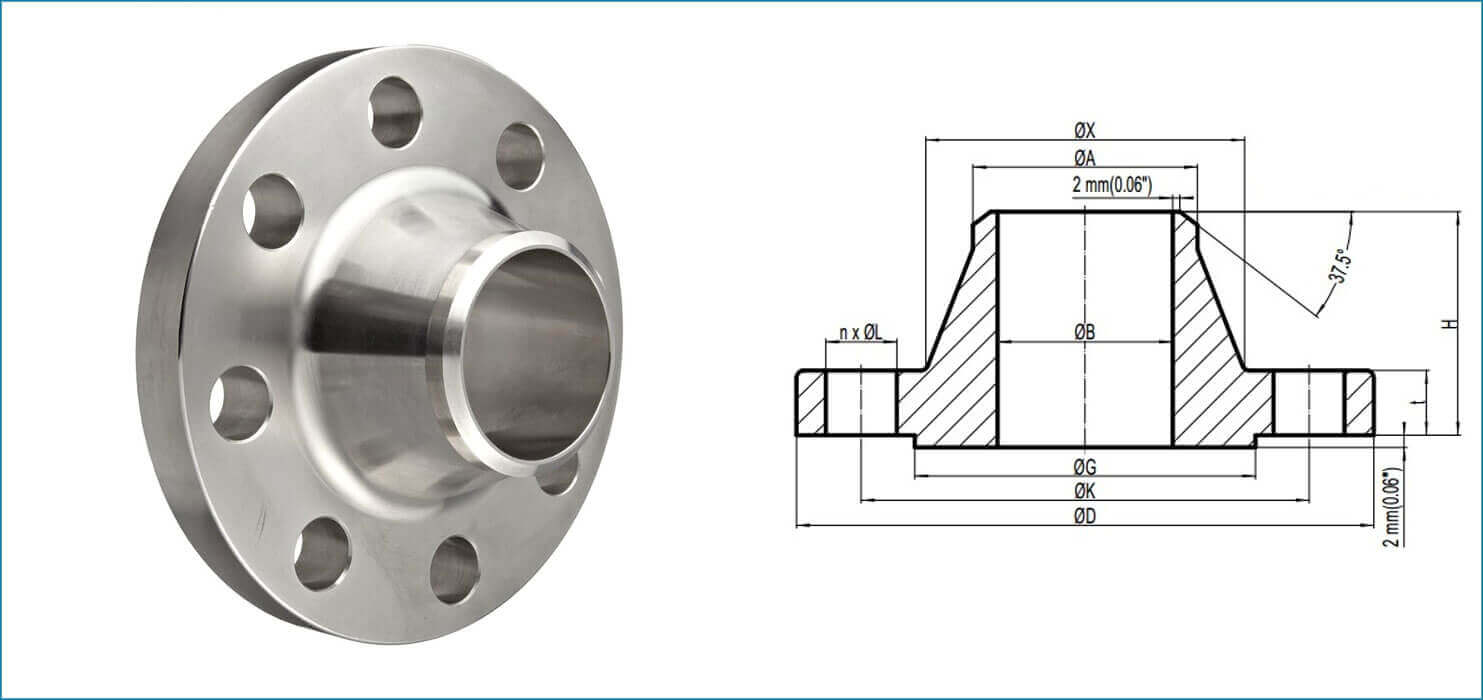
5. Dimensions and Tolerances
The dimensions of weld neck pipe flanges are standardized under ANSI B16.5.
Comprehensive Dimensions Table
| NPS (inches) | OD (inches) | Bolt Circle Diameter (inches) | Bolt Hole Diameter (inches) | Flange Thickness (inches) | Hub Diameter at Base (inches) | Raised Face Height (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ½ | 3.5 | 2.375 | 0.625 | 0.44 | 1.06 | 1/16 |
| 1 | 4.25 | 3.125 | 0.625 | 0.56 | 1.38 | 1/16 |
| 4 | 9 | 7.5 | 0.75 | 0.94 | 4.81 | 1/16 |
| 8 | 13.5 | 11.75 | 1.00 | 1.44 | 9.06 | 1/4 |
6. Pressure-Temperature Ratings
Weld neck flanges are classified into pressure classes, ranging from 150# to 2500#.
Pressure-Temperature Ratings Table
| Class | Temp (°F) | Carbon Steel (psi) | Stainless Steel (psi) | Alloy Steel (psi) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 100 | 285 | 275 | 290 |
| 300 | 100 | 740 | 720 | 760 |
| 600 | 100 | 1480 | 1440 | 1520 |
| 1500 | 100 | 3705 | 3600 | 3800 |
| 2500 | 100 | 6170 | 6000 | 6250 |
7. Facing Types for Weld Neck Pipe Flanges
Raised Face (RF)
- Standard height: 1/16″ for ≤400#, 1/4″ for >400#.
- Improves gasket compression.
Flat Face (FF)
- Used with flat gaskets in low-pressure applications.
Ring Type Joint (RTJ)
- Ensures leak-proof seals in high-pressure systems.
8. Manufacturing Process
Weld neck flanges are manufactured through forging and machining processes.
- Material Selection: Raw materials are chosen based on specifications.
- Forging: High-temperature shaping ensures strength and durability.
- Machining: Precision drilling, threading, and surface finishing.
- Heat Treatment: Stress relief and strengthening processes.
- Inspection: Dimensional checks and non-destructive testing.
9. Applications of Weld Neck Flanges
Weld neck flanges are used in:
- Oil and Gas: Pipelines under high pressure and temperature.
- Petrochemical Plants: For handling hazardous chemicals.
- Power Generation: Steam lines in high-temperature systems.
- Marine Systems: Offshore platforms and saltwater pipelines.
10. Advantages of Using Weld Neck Flanges
- High Strength: The tapered hub design provides excellent mechanical integrity.
- Leak Prevention: Full penetration welding ensures a robust, leak-proof seal.
- Extended Lifespan: With proper maintenance, these flanges last decades.
- Stress Distribution: Minimizes concentrated stress at the flange base.
11. Comparison with Other Flange Types
| Feature | Weld Neck | Slip-On | Socket Weld | Blind |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | High | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Strength | High | Moderate | High | High |
| Installation Ease | Moderate | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Leak Resistance | Excellent | Moderate | Moderate | Excellent |
12. Installation and Welding Guidelines
- Preparation: Ensure pipe and flange alignment.
- Welding: Perform full penetration welding for maximum strength.
- Inspection: Check welds for porosity and cracks.
13. Inspection and Maintenance Procedures
- Visual Inspection: Look for cracks, corrosion, or misalignment.
- Pressure Testing: Regular hydrostatic tests to detect leaks.
- Cleaning: Remove debris and buildup to prevent corrosion.
14. Environmental and Economic Considerations
Economic Factors
- High initial cost offset by reduced maintenance needs.
Environmental Impact
- Recycling of materials minimizes waste.
- Adherence to eco-friendly manufacturing standards.
15. Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary advantage of a weld neck flange?
Its strength and stress-distributing design make it ideal for high-pressure systems.
2. Are weld neck flanges compatible with other standards?
Yes, they comply with both ANSI and ASME standards.
3. What is the typical lifespan of a weld neck flange?
With proper maintenance, it can last for decades.
4. How are weld neck flanges tested?
Hydrostatic and ultrasonic tests are commonly performed.
5. Can I use weld neck flanges in corrosive environments?
Yes, with appropriate material selection such as stainless steel or duplex alloys.
6. What are the common facing types?
Raised Face (RF), Flat Face (FF), and Ring Type Joint (RTJ).
Conclusion
The ANSI B16.5 Weld Neck Pipe Flange is a cornerstone of high-pressure piping systems, offering unmatched strength, durability, and performance. Whether for oil and gas, petrochemical, or power generation applications, weld neck flanges are engineered to meet the most demanding specifications.




You must be logged in to post a comment.