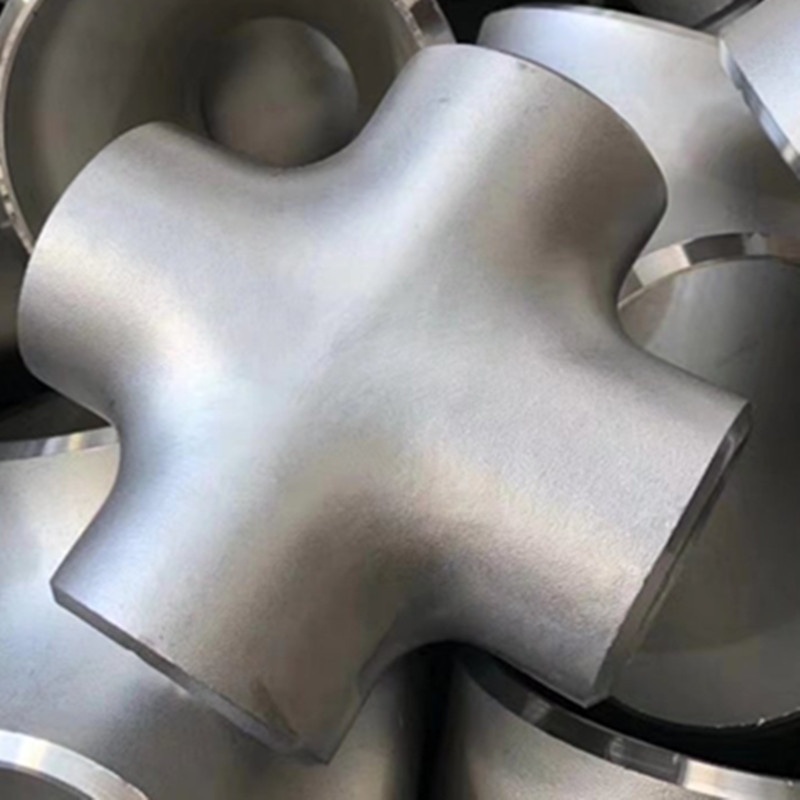

ASME B16.5 Stainless Steel 304/316/904L Butt Weld Pipe Fitting Cross refers to a specific type of pipe fitting that adheres to standards set by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). Here, let’s break down each part of this term:
-
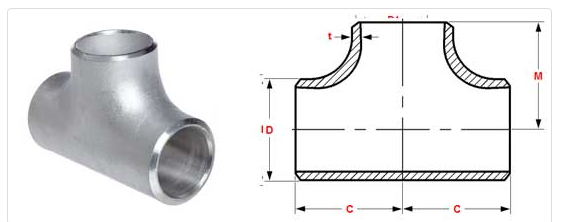
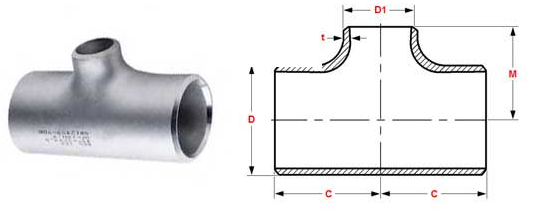
ASME B16.5: This refers to the specific standard set by the ASME, which focuses on pipe flanges and flanged fittings. These standards cover pressure-temperature ratings, materials, dimensions, tolerances, marking, and testing for flanges and flanged fittings in sizes NPS 1/2 through NPS 24, and flanged fittings with rating class designation 150 and 300.
-
Stainless Steel 304/316/904L: This refers to the material of the pipe fitting. All three grades (304, 316, and 904L) are types of stainless steel, which is prized for its resistance to corrosion. 304 is a basic stainless steel that is widely used for various applications. 316 has an added molybdenum content that gives it greater resistance to corrosion, especially from chlorides like sea water. 904L has an even higher resistance to corrosion and is typically used in severe environments.
-
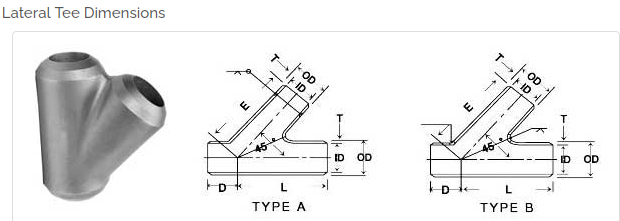
Butt Weld Pipe Fitting Cross: This is the specific type of fitting being referred to. A butt weld pipe fitting cross (also known as a four-way fitting) is a type of fitting that has four openings, which can be either outlets or inlets. The butt weld aspect refers to the way the fitting is attached to the pipes: the ends of the pipes and the ends of the fitting are made to match exactly, and are then welded together.
This type of fitting is often used in industries that require sturdy and leak-proof systems, such as the petrochemical industry, the oil and gas industry, and the water supply industry. It is important to note that the choice of material (304, 316, or 904L) would depend on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of fluid being transported and the environmental conditions.



You must be logged in to post a comment.